The concept of remote automation control has transformed industries worldwide, with IoT devices playing a pivotal role. From enhancing efficiency to providing real-time monitoring, IoT devices have become indispensable in enabling remote operations and intelligent automation. This blog delves into the various aspects of how IoT devices contribute to remote automation control, explores their applications across industries, and discusses the challenges and future prospects of this technology.
What Are IoT Devices and Remote Automation Control?
IoT (Internet of Things) devices are physical objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity features that enable them to collect and exchange data. These devices can connect to the internet, communicate with each other, and interact with centralized control systems, enabling automation and monitoring of processes without human intervention.
Remote automation control, on the other hand, allows users to manage and control systems or devices from distant locations through internet-enabled platforms. By integrating IoT devices into automation systems, industries can optimize operations and respond to issues in real time, even from thousands of miles away.
Core Components of IoT Devices in Automation
To understand how IoT devices enable remote automation control, it is essential to examine their core components:
1. Sensors
Sensors are the foundation of IoT devices, as they collect real-time data from the environment, such as temperature, pressure, and motion.
2. Actuators
Actuators receive commands from the central system and execute actions, such as opening a valve or turning on a motor.
3. Connectivity Modules
Connectivity modules enable devices to communicate with other systems or platforms via protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or Zigbee.
4. Processors and Microcontrollers
Processors interpret data collected by sensors and make decisions based on pre-programmed logic.
5. Power Supply Units
Power is critical for IoT devices, whether sourced from batteries, solar panels, or direct connections.
Applications of IoT Devices in Remote Automation Control
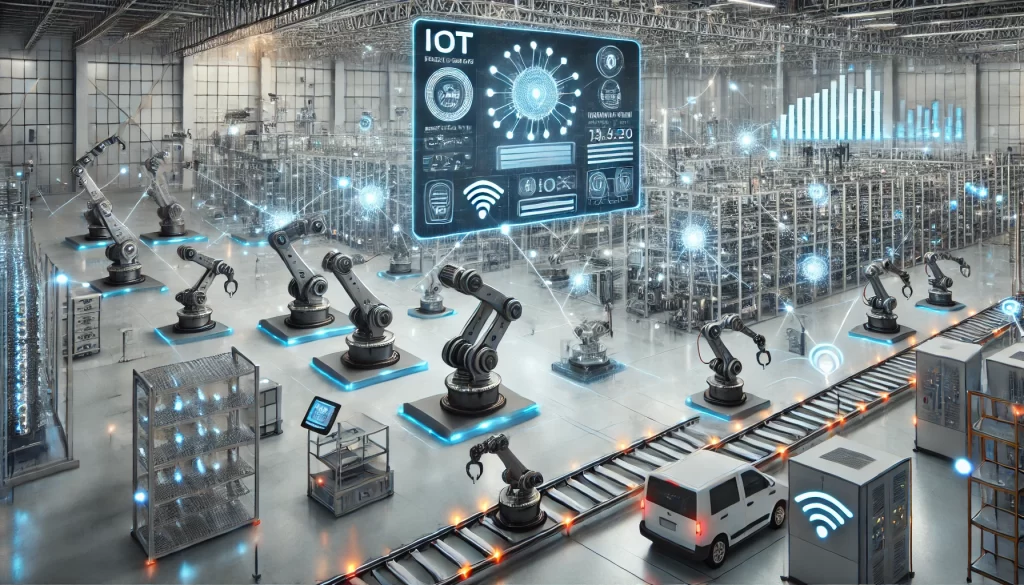
1. Smart Manufacturing
IoT devices allow manufacturers to automate production lines, monitor equipment health, and reduce downtime through predictive maintenance.
Example:
A smart factory equipped with IoT sensors can identify potential equipment failures before they occur, enabling timely interventions and avoiding costly disruptions.
2. Energy Management
IoT-enabled automation systems in energy plants optimize resource utilization and monitor energy consumption remotely.
Example:
Smart grids use IoT devices to monitor electricity demand and adjust supply dynamically, reducing waste and ensuring efficiency.
3. Agriculture
IoT devices in agriculture enable automated irrigation, pest control, and soil monitoring, improving crop yield and resource management.
Example:
A smart irrigation system equipped with IoT sensors measures soil moisture levels and adjusts water flow accordingly.
4. Healthcare
Remote patient monitoring has gained prominence, with IoT devices tracking vital signs and sending real-time data to healthcare providers.
Example:
Wearable devices like smartwatches monitor heart rate and oxygen levels, alerting doctors in case of anomalies.
5. Smart Cities
IoT devices automate and optimize urban infrastructure, including traffic management, waste disposal, and public safety.
Example:
Smart traffic lights equipped with IoT sensors adjust their timing based on real-time traffic data to reduce congestion.

Key Benefits of IoT Devices in Remote Automation
1. Real-Time Monitoring and Control
IoT devices collect and transmit data instantaneously, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and prevent operational failures.
2. Enhanced Efficiency
Automation reduces manual intervention, leading to faster processes, minimized errors, and increased productivity.
3. Cost Savings
Remote monitoring and predictive maintenance lower operational costs by reducing downtime and energy consumption.
4. Flexibility and Scalability
IoT systems can be easily scaled to include more devices or accommodate changing business needs.
5. Improved Safety
IoT devices enable the monitoring of hazardous environments, ensuring worker safety and compliance with regulations.
Technological Framework of IoT Devices in Remote Automation
1. Communication Protocols
IoT devices rely on various communication protocols for seamless data exchange.
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport): Lightweight protocol ideal for low-bandwidth networks.
- CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol): Designed for constrained devices in IoT ecosystems.
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): Standard protocol for internet communication.
2. Cloud Platforms
Cloud platforms store and analyze data collected by IoT devices, providing actionable insights and enabling centralized control.
3. Edge Computing
Edge computing processes data closer to the source (the IoT device), reducing latency and bandwidth usage.
Challenges in Implementing IoT-Based Remote Automation
Despite its numerous benefits, implementing IoT in remote automation comes with challenges:
1. Security Concerns
IoT devices are vulnerable to cyberattacks, requiring robust security measures to protect data and systems.
2. Data Management
The vast amount of data generated by IoT devices can overwhelm systems without proper storage and processing solutions.
3. Connectivity Issues
Reliable internet connectivity is essential for IoT devices, and disruptions can hinder operations.
4. Cost of Implementation
Setting up IoT systems requires a significant initial investment, making it challenging for small businesses.
Future of IoT Devices in Remote Automation Control (2024 and Beyond)
1. AI Integration
IoT systems are increasingly integrating artificial intelligence for predictive analytics and autonomous decision-making.
2. 5G Connectivity
The adoption of 5G networks will enhance the speed and reliability of IoT communication.
3. Blockchain for Security
Blockchain technology is being explored to secure IoT devices and ensure transparent data transactions.
4. Sustainable Solutions
Eco-friendly IoT devices powered by renewable energy sources will become more prevalent.

Case Study: Aknitech Automation’s IoT Solutions
Aknitech Automation is at the forefront of leveraging IoT devices for remote automation control. By integrating smart sensors and advanced connectivity protocols, the company has enabled industries to achieve operational excellence. Their IoT solutions ensure real-time monitoring, enhanced productivity, and secure data management, making them a leader in the automation sector.
Conclusion
IoT devices have become a cornerstone of remote automation control, offering unprecedented advantages across industries. As technology advances, the integration of IoT with AI, 5G, and blockchain will further unlock its potential. Companies like Aknitech Automation are pioneering these innovations, ensuring that industries remain competitive and efficient in the digital age.
With IoT, the future of remote automation is not just promising—it’s here.