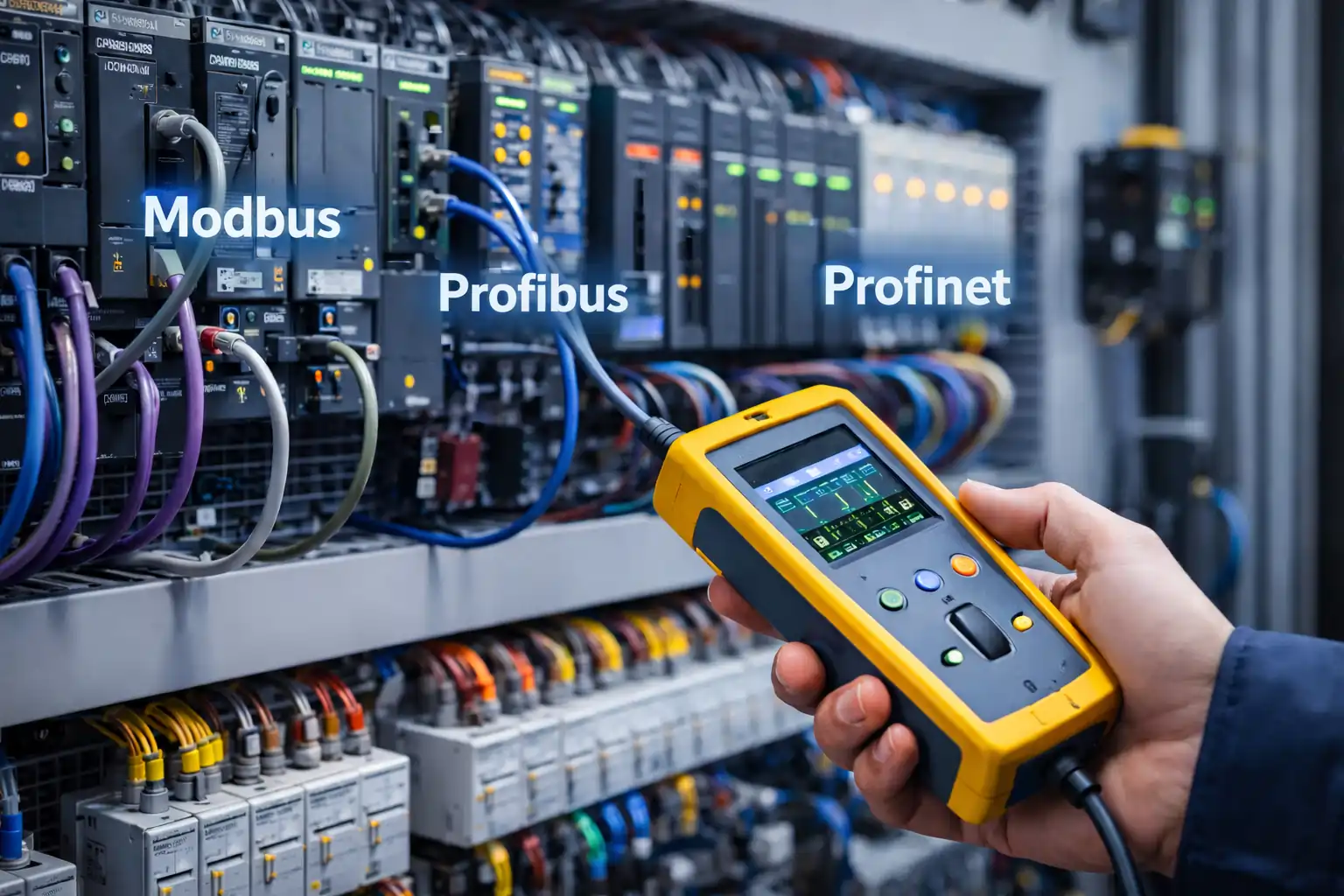
Industrial automation is transforming rapidly, powered by new technologies and the demand for smarter, more efficient systems. As industries worldwide strive to enhance productivity and reduce operational costs, key trends are emerging that promise to redefine automation as we know it. Let’s explore these critical trends and see what the future of industrial automation holds.
1. Advanced Robotics and Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Collaborative Robots (Cobots) are designed to work alongside human operators safely. Unlike traditional robots, which are often kept separate from humans for safety reasons, cobots are programmed to be sensitive to human presence and movement, making them ideal for working in close proximity to employees.
- Key Benefits of Cobots:
- Enhanced productivity through collaboration with human workers.
- Improved workplace safety due to responsive and adaptable programming.
- Cost-effectiveness in automating repetitive, mundane tasks without the need for complex installations.
- Applications in Manufacturing: Cobots are already being used in assembly lines, product handling, packaging, and quality inspections, among others.

2. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
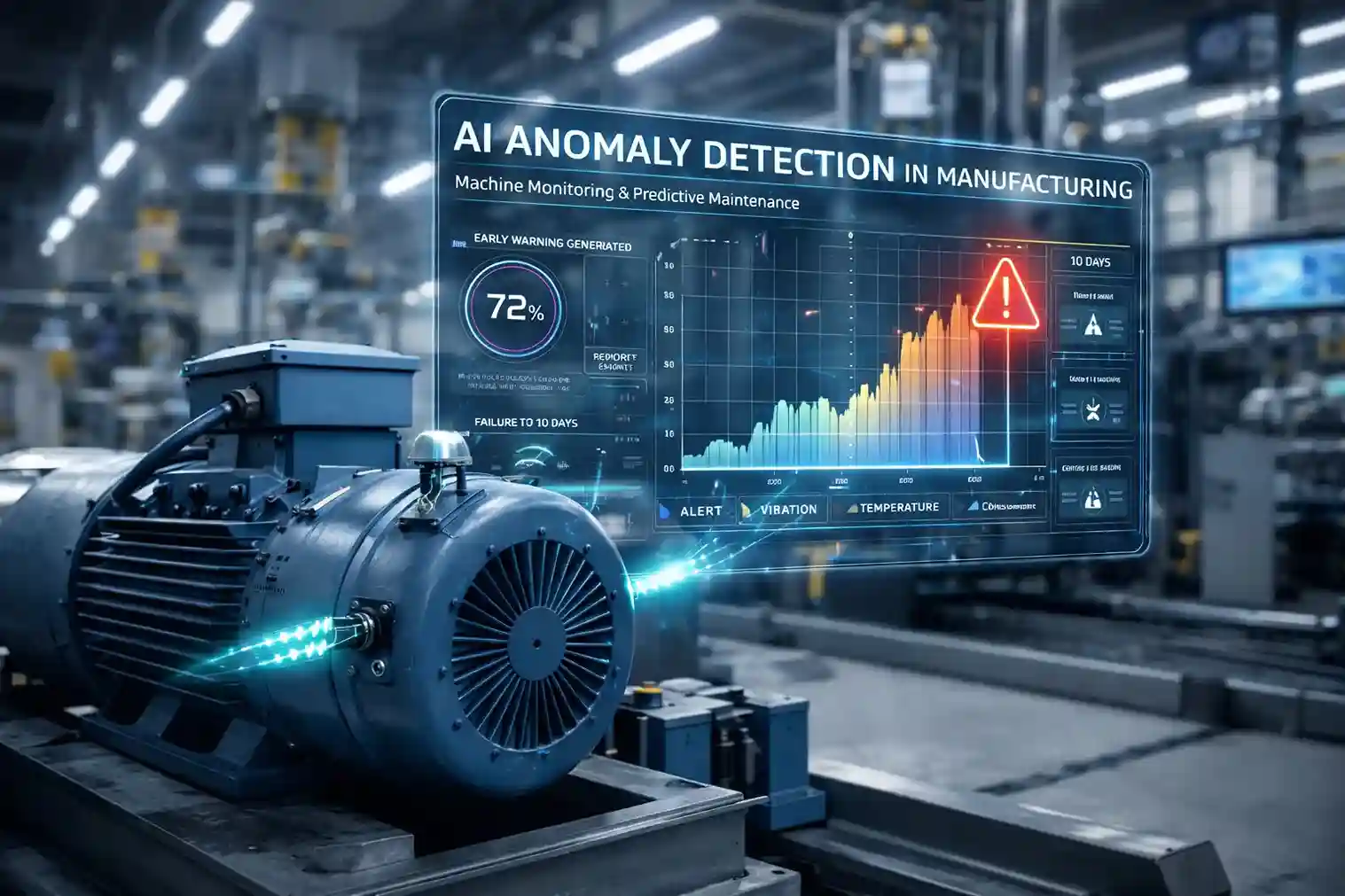
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) connects devices, machines, and equipment on a centralized network, allowing for real-time data exchange and monitoring. This trend is foundational in transitioning traditional factories to smart factories.
- Advantages of IIoT:
- Real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance to avoid unplanned downtime.
- Enhanced quality control with detailed data on machine performance and output.
- Better data-driven decision-making through comprehensive analytics.
- Future of IIoT: With 5G connectivity advancing, IIoT will become faster and more reliable, facilitating more widespread integration into factories and industrial settings.
3. Edge Computing for Real-Time Processing
As the number of connected devices grows, so does the volume of data they generate. Edge computing is becoming crucial as it processes data locally rather than sending it to a centralized cloud, reducing latency and ensuring faster decision-making.
- Edge Computing Benefits:
- Reduced response times for real-time decision-making in critical situations.
- Lower bandwidth requirements and reduced dependency on internet connectivity.
- Improved data security, as sensitive information can be processed closer to its source.
- Practical Applications: Edge computing is being used in time-sensitive applications such as quality control, predictive maintenance, and even automated safety shutdowns.
4. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML in industrial automation focus on improving system efficiency, predicting issues before they arise, and optimizing production processes. This is particularly beneficial in scenarios that require adaptability and rapid analysis.
- AI/ML Capabilities:
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can analyze historical data to predict when a machine will need maintenance, preventing unexpected downtime.
- Quality Control: ML algorithms can detect defects in products at a faster rate than manual inspections.
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI helps in forecasting demand and managing inventory based on trends, ensuring materials are available when needed.
- Future Prospects: AI and ML will continue to evolve, allowing for more sophisticated automation systems that learn and improve over time, contributing to greater productivity and lower operational costs.
5. Digital Twins and Simulation
Digital twins create a virtual model of a physical system, which can be used to simulate and test various scenarios before making real-world changes. This helps industries anticipate potential issues, optimize processes, and reduce errors.
- Uses of Digital Twins:
- Predicting machine behavior to prevent failures and optimize efficiency.
- Simulating factory floor changes, like equipment placement, to optimize workflow.
- Training new employees in a risk-free virtual environment.
- Growth Potential: Digital twin technology is expected to become standard practice for companies looking to implement highly efficient automation and process improvements.
6. 5G Connectivity
The 5G network significantly enhances data speed and reliability, enabling seamless communication between devices, machines, and systems. This development is essential for the real-time data sharing and low-latency responses required in modern industrial automation.
- 5G Advantages in Automation:
- Supports large-scale IoT implementations, providing connectivity to thousands of devices within a factory.
- Ensures rapid data exchange, which is crucial for time-sensitive operations such as remote monitoring and control.
- Reduces costs associated with wired connections, making it easier to expand automation capabilities.
- Future Applications: With its low-latency communication, 5G will be a major driver for smart factories, allowing real-time data sharing and monitoring of machines, assets, and processes.
7. Cybersecurity for Industrial Systems
As industrial systems become more interconnected, cybersecurity becomes a top priority. Protecting these systems from cyber threats is essential to prevent operational disruptions, financial losses, and data breaches.
- Cybersecurity Strategies:
- Using secure networks and encrypted communications.
- Implementing access control to prevent unauthorized access.
- Utilizing AI-powered threat detection systems to monitor network activity and detect anomalies.
- Expected Trends: Cybersecurity will evolve alongside automation, with predictive threat detection and AI-based risk management tools becoming standard to secure critical infrastructure.
8. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, offers unique benefits for industrial automation by allowing customized parts to be created on demand. This technology minimizes inventory costs, speeds up the prototyping process, and enables the production of complex parts that traditional manufacturing cannot achieve.
- Benefits of Additive Manufacturing:
- Allows rapid prototyping for new products or components.
- Reduces material waste compared to traditional subtractive manufacturing.
- Facilitates localized production, reducing reliance on complex supply chains.
- Future Outlook: As 3D printing technology advances, it will become increasingly integrated into production lines, enabling on-demand manufacturing and greater flexibility in product design.
9. Augmented Reality (AR) for Maintenance and Training
Augmented Reality (AR) is proving valuable in maintenance, training, and remote support within industrial settings. By overlaying digital information onto physical systems, AR enables workers to perform complex tasks with greater accuracy.
- AR Applications:
- Maintenance: Technicians can view a virtual overlay showing step-by-step repair instructions.
- Training: AR provides new employees with hands-on, interactive learning experiences without disrupting the actual production process.
- Remote Support: Experts can guide on-site workers through troubleshooting processes remotely.
- Future of AR in Industry: As AR hardware and software become more sophisticated, its applications in maintenance and employee training will continue to expand.

10. Human-Machine Interface (HMI) Enhancements
Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) are evolving to include touchscreens, gesture recognition, and even voice commands, making it easier for operators to control complex machinery. Advanced HMIs are improving the efficiency of industrial systems by enabling more intuitive user interactions.
- Modern HMI Features:
- Touchscreen controls for faster and easier machine interaction.
- Voice command capabilities for hands-free operation.
- Enhanced graphics for clearer data visualization.
- Future Implications: HMI improvements will make industrial automation more accessible and user-friendly, allowing operators to monitor and control systems more effectively.
Conclusion
The future of industrial automation is set to be shaped by numerous trends that promise to drive efficiency, reduce costs, and optimize workflows. From collaborative robots to IIoT, 5G connectivity, cybersecurity, and AI-driven insights, these trends are creating a new era of smart factories. Companies like Aknitech Automation are at the forefront of implementing these advanced solutions, providing industries with the tools to adapt and thrive in a rapidly evolving landscape.
As automation technologies evolve, the integration of digital twins, AR, and additive manufacturing will provide unparalleled opportunities for simulation, training, and customization. The impact of these developments will reshape industrial processes, ensuring that industries can meet the growing demands of modern markets with efficiency, safety, and agility.